Middle Level Science (Grades 5–8)
Subtest 2 Sample Items
Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Expand All | Collapse All
Question 1
1. Single cell animals respire by exchanging gases with the surrounding environment across their cell membranes. The evolution of more sophisticated respiratory systems was necessary in multicellular organisms because as the size of an organism increases:
- the synthesis of ATP requires more steps.
- surface area increases more slowly than volume.
- replication of large amounts of DNA requires more oxygen.
- production of waste gases increases exponentially.
Answer to question 1
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0008) Due to the large surface-area-to-volume ratio of single cells, unicellular organisms are able to obtain oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide by way of diffusion across the cell membrane. Multicellular organisms must also exchange gases with the atmosphere in order to survive; however, they have a much smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio. In order for gas exchange to occur at a rate that will support the quantity of gas needed for life processes, multicellular organisms developed complex respiratory organs and structures with large surface areas (e.g., the alveoli in the lungs, plant leaves), which greatly increase the amount of gas exchange that can occur.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0008) Due to the large surface-area-to-volume ratio of single cells, unicellular organisms are able to obtain oxygen and excrete carbon dioxide by way of diffusion across the cell membrane. Multicellular organisms must also exchange gases with the atmosphere in order to survive; however, they have a much smaller surface-area-to-volume ratio. In order for gas exchange to occur at a rate that will support the quantity of gas needed for life processes, multicellular organisms developed complex respiratory organs and structures with large surface areas (e.g., the alveoli in the lungs, plant leaves), which greatly increase the amount of gas exchange that can occur.
Question 2
2. As shown in the diagram, the xylem tissue of angiosperms contains overlapping tracheid cells that have small holes in their secondary cell walls called pits.
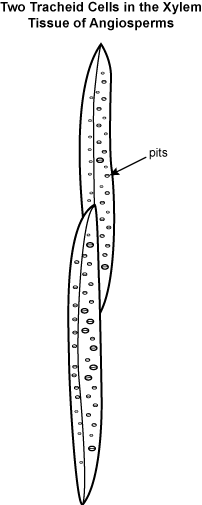
The surface of each cell is covered in many small holes called pits along its surface
The primary function of the pits in the tracheid cells of xylem tissue is to:
- allow the exchange of gases between xylem and the surrounding environment.
- promote the flow of nutrient-rich fluids between the xylem and phloem.
- support the active transport of nutrients in the xylem against an osmotic gradient.
- facilitate the movement of water and dissolved minerals in the xylem.
Answer to question 2
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0008) The xylem tissue in vascular plants functions to transport water and dissolved minerals throughout the plant. The elongated tracheid cells in xylem tissue are covered in small holes called pits that allow the passage of water and dissolved minerals between overlapping tracheid cells. When fully functional, tracheid cells are dead and the holes in their secondary cell walls create an interconnected system for transporting water and dissolved minerals. Tracheid cells are bundled together in vascular bundles that occur throughout the nonwoody parts of a vascular plant and provide some structural support in addition to transporting water from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0008) The xylem tissue in vascular plants functions to transport water and dissolved minerals throughout the plant. The elongated tracheid cells in xylem tissue are covered in small holes called pits that allow the passage of water and dissolved minerals between overlapping tracheid cells. When fully functional, tracheid cells are dead and the holes in their secondary cell walls create an interconnected system for transporting water and dissolved minerals. Tracheid cells are bundled together in vascular bundles that occur throughout the nonwoody parts of a vascular plant and provide some structural support in addition to transporting water from the roots to the rest of the plant.
Question 3
3. Which of the following changes in the healthy functioning of the human body is the direct trigger for a stroke?
- disruption of the normal electrical activity in the frontal lobe of the brain
- buildup of plaque in the arteries that limits the flow of oxygen and nutrients to the heart
- interruption in the normal supply of oxygenated blood to a region of the brain
- damage to the capillaries that supply the heart muscle with an oxygen-rich blood supply
Answer to question 3
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0008) The uninterrupted supply of oxygen to the brain via the circulatory system is an essential component of the healthy functioning of an organism. Since even a short interruption of oxygenated blood to the brain can produce brain damage, strokes are a serious medical emergency that can cause permanent neurological damage, paralysis, and death.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0008) The uninterrupted supply of oxygen to the brain via the circulatory system is an essential component of the healthy functioning of an organism. Since even a short interruption of oxygenated blood to the brain can produce brain damage, strokes are a serious medical emergency that can cause permanent neurological damage, paralysis, and death.
Question 4
4. Passive and active immunity are components of the human immune system. The characteristic of active immunity that distinguishes it from passive immunity is that active immunity:
- destroys nonspecific pathogens present in the body regardless of prior disease exposure.
- develops over time in response to exposure to an infectious pathogen or vaccination.
- provides disease protection for newborns before the immune system is fully developed.
- uses antibodies from a mother's immune system to fight disease in a developing fetus.
Answer to question 4
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0008) Active immunity is also called adaptive immunity because it depends on the response of the infected person's immune system to an infection. This contrasts with passive immunity, which occurs when antibodies from one person are passed to another, such as when IgA antibodies are transferred to a nursing infant in breast milk.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0008) Active immunity is also called adaptive immunity because it depends on the response of the infected person's immune system to an infection. This contrasts with passive immunity, which occurs when antibodies from one person are passed to another, such as when I g A antibodies are transferred to a nursing infant in breast milk.
Question 5
5. Leukemia is a type of cancer of the blood. It results in high numbers of abnormal white blood cells that do not function correctly. Which of the following components of the immune system is likely to be the site of the initial development of the disease?
- spleen
- lymph nodes
- tonsils
- bone marrow
Answer to question 5
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0008) For many white blood cells to be produced, the mutations that cause their overproduction must be in the stem cells from which the white blood cells originate. Since multipotent stem cells in the bone marrow can mature into all of the blood cell types, bone marrow is therefore the most likely site of development for this disease.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0008) For many white blood cells to be produced, the mutations that cause their overproduction must be in the stem cells from which the white blood cells originate. Since multipotent stem cells in the bone marrow can mature into all of the blood cell types, bone marrow is therefore the most likely site of development for this disease.
Question 6
6. The diagram below shows a strand of a ribosome and its mRNA.
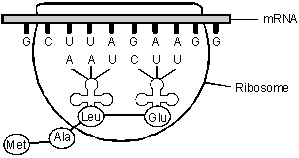
From left to right, the RNA contains components labeled G, C, U, U, A, G, A, A, G, and G. Two molecules are near this strand. One contains, from left to right, the units C, U, and U. The other molecule contains, from left to right, the units A, A, U. The C, U, and U of the first molecule are in the process of aligning with the G, A, and A of the messenger RNA. The A, A, and U of the second molecule are in the process of aligning with the U, U, and A of the messenger RNA. Below these two molecules, a protein is being formed. So far it contains the amino acids G L U, L E U, A L A, and M E T.
Which of the following processes does this diagram best represent?
- RNA transcription
- active transport
- DNA replication
- protein synthesis
Answer to question 6
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0009) The process of protein synthesis involves the transfer of information coded in DNA to an RNA intermediate, known as messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA codes for the assembly of a specific protein. Every set of three nucleic acids on the mRNA is called a codon. Each codon is recognized by a specific transfer RNA (tRNA), which itself is shaped roughly like a plus sign. One end of the tRNA recognizes the mRNA and the other end carries an amino acid. The ribosome is a cellular structure that coordinates the pairing of the mRNA codons with each tRNA and facilitates the linking of amino acids that are carried by the tRNA. As the amino acids are linked one by one by the ribosome, they form the growing peptide chain. This peptide chain is what will ultimately become folded to form a protein molecule.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0009) The process of protein synthesis involves the transfer of information coded in DNA to an RNA intermediate, known as messenger RNA (mRNA). The mRNA codes for the assembly of a specific protein. Every set of three nucleic acids on the mRNA is called a codon. Each codon is recognized by a specific transfer RNA (tRNA), which itself is shaped roughly like a plus sign. One end of the tRNA recognizes the mRNA and the other end carries an amino acid. The ribosome is a cellular structure that coordinates the pairing of the mRNA codons with each tRNA and facilitates the linking of amino acids that are carried by the tRNA. As the amino acids are linked one by one by the ribosome, they form the growing peptide chain. This peptide chain is what will ultimately become folded to form a protein molecule.
Question 7
7. The diagram below shows a cross section of the cell membrane of an animal cell. The large molecule identified by the arrow is a protein embedded in the cell membrane.
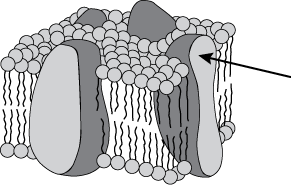
An arrow indicates a large protein shape completely transecting the phospholipid bilayer.
Which of the following is a major function of proteins embedded in the cell membrane?
- transporting of substances in and out of the cell
- generating energy needed for cell respiration
- destroying pathogens surrounding the cell
- producing nucleic acids that direct cell division
Answer to question 7
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0009) Protein molecules embedded in the cell membrane serve a number of important functions in the cell, including joining cells together, facilitating cellular reactions, maintaining cell shape, and transporting substances in and out of the cell.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0009) Protein molecules embedded in the cell membrane serve a number of important functions in the cell, including joining cells together, facilitating cellular reactions, maintaining cell shape, and transporting substances in and out of the cell.
Question 8
8. A characteristic of meiosis that distinguishes it from mitosis is that meiosis:
- involves the production of a cell that is genetically identical to the parent cell.
- requires RNA to build proteins needed in the formation of a new cell.
- produces daughter cells with half as many chromosomes as the parent cell.
- involves the duplication of chromosomes during the interphase stage of the cell cycle.
Answer to question 8
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0009) Meiosis is a type of cell division carried out in sexually reproducing organisms in which the cell undergoes two divisions with only one replication of genetic material. Meiosis results in the production of haploid daughter cells that have half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell. These daughter cells are called gametes and the fusing of two gametes in sexual reproduction is called fertilization. Unlike meiosis, mitosis produces diploid daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell and are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0009) Meiosis is a type of cell division carried out in sexually reproducing organisms in which the cell undergoes two divisions with only one replication of genetic material. Meiosis results in the production of haploid daughter cells that have half the number of chromosomes of the original parent cell. These daughter cells are called gametes and the fusing of two gametes in sexual reproduction is called fertilization. Unlike meiosis, mitosis produces diploid daughter cells that have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell and are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Question 9
9. Use the passage below to answer the question that follows.
In the Early Devonian age, plants were small and grew slowly via turgor pressure in parenchyma cells. By the Middle Devonian, plants had developed heavily thickened sclerenchyma cells, allowing plants to reach great heights with highly branched architectures. However, the sclerenchyma cells blocked sunlight from tissues growing beneath, limiting the broadening of leaves. By the Late Devonian, collenchyma cells evolved. These cells allowed for growing plants to form structures that allowed for plants to better compete with other plants occupying the same niche.
Which of the following structures allows for collenchyma cells to best aid the development of growing plants in the competitive environment of the Late Devonian?
- thick translucent cell walls capable of elongation
- small vacuoles
- several wide porins that increase nutrient transport
- many chloroplasts
Answer to question 9
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0009) Collenchyma cells provide structure to the young growing plant with their thick but flexible cell walls. Unlike heavily lignified sclerenchyma cell walls, the cell walls of collenchyma cells are translucent, which allows for new cells to develop beneath layers of developed cells. Through having an elongated shape, as well as the ability to resume meristematic activity, collenchyma cells can also repair tissue damage done to easily grazed-upon young plants.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0009) Collenchyma cells provide structure to the young growing plant with their thick but flexible cell walls. Unlike heavily lignified sclerenchyma cell walls, the cell walls of collenchyma cells are translucent, which allows for new cells to develop beneath layers of developed cells. Through having an elongated shape, as well as the ability to resume meristematic activity, collenchyma cells can also repair tissue damage done to easily grazed-upon young plants.
Question 10
10. Human height is regulated by multiple genes in combination with environmental factors which determine whether an individual is a tall, medium, or short height. Assuming that height is determined by at least two genes, which of the following inheritance patterns best describes height?
- mitochondrial
- codominant
- recessive
- polygenic
Answer to question 10
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0009) Polygenic inheritance is associated with a phenotypic trait that shows a pattern of continuous variation. The inheritance of this type of a trait can't be predicted using a model based on one or two gene combinations, but instead is the result of small combinations by many genes.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0009) Polygenic inheritance is associated with a phenotypic trait that shows a pattern of continuous variation. The inheritance of this type of a trait can't be predicted using a model based on one or two gene combinations, but instead is the result of small combinations by many genes.
Question 11
11. A number of mammals living in temperate climate zones hibernate for long periods during the winter. During hibernation, which of the following changes occurs in these mammals?
- heightened responsiveness to external stimuli
- increase in the body's core temperature
- reduction in the basal metabolic rate
- dehydration of nonessential body tissues
Answer to question 11
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0010) Hibernation during winter is a physiological adaptation that helps an organism survive long periods of cold temperature and low food availability. Characteristics of hibernation include reduced metabolic rate, slowing of the heart and respiratory rate, and reduced body temperature.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0010) Hibernation during winter is a physiological adaptation that helps an organism survive long periods of cold temperature and low food availability. Characteristics of hibernation include reduced metabolic rate, slowing of the heart and respiratory rate, and reduced body temperature.
Question 12
12. Which of the following factors is positively correlated with increased diversity of land species?
- distance from the geographical poles
- diurnal temperature range
- nutrient and mineral content of soils
- elevation above sea level
Answer to question 12
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0010) The variety of different land species generally decreases from high levels in the tropics to relatively low levels in polar regions. Many of the world's highest concentrations of different species occur in tropical "biodiversity hotspots," such as Brazil's Atlantic rain forest and the island of Madagascar.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0010) The variety of different land species generally decreases from high levels in the tropics to relatively low levels in polar regions. Many of the world's highest concentrations of different species occur in tropical "biodiversity hotspots," such as Brazil's Atlantic rain forest and the island of Madagascar.
Question 13
13. Which of the following functions is served by the single-celled algae that live within reef-forming corals?
- protecting corals from ultraviolet radiation in sunlight
- providing most of the nutrients required for coral growth
- producing the toxins that corals use to kill their prey
- generating carbonate casings to protect corals from predators
Answer to question 13
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0010) Corals are small animals that live in calcium carbonate shells in tightly clustered colonies. Photosynthetic single-celled algae reside within corals providing corals with most of their nutrition, but also limiting the corals to the ocean's photic zone where sufficient light is available for photosynthesis. The calcium carbonate structure secreted by colonies of these coral organisms is called a coral reef and is one of the most biologically diverse habitats in the world.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0010) Corals are small animals that live in calcium carbonate shells in tightly clustered colonies. Photosynthetic single-celled algae reside within corals providing corals with most of their nutrition, but also limiting the corals to the ocean's photic zone where sufficient light is available for photosynthesis. The calcium carbonate structure secreted by colonies of these coral organisms is called a coral reef and is one of the most biologically diverse habitats in the world.
Question 14
14. The hawthorn fly, native to North America, historically fed on hawthorn fruit. However, a distinct population emerged in the 19th century after the introduction of the non-native apple. The new population of flies does not feed on hawthorn fruit and the original population of flies does not feed on apples, although both populations occupy the same geographical location. This an example of:
- Müllerian mimicry.
- character displacement.
- sympatric speciation.
- stabilizing selection.
Answer to question 14
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0010) In order for such divergence to occur in a population of organisms, there must be a reduced gene flow between portions of the population such that genetic differences arise. Sympatric speciation refers to a mode of speciation in which the new species is formed within the geographic range of the original population. In the case of the hawthorn fly, the shift to a new niche (the non-native apple) resulted in a reduced gene flow and two distinct populations of hawthorn fly.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0010) In order for such divergence to occur in a population of organisms, there must be a reduced gene flow between portions of the population such that genetic differences arise. Sympatric speciation refers to a mode of speciation in which the new species is formed within the geographic range of the original population. In the case of the hawthorn fly, the shift to a new niche (the non-native apple) resulted in a reduced gene flow and two distinct populations of hawthorn fly.
Question 15
15. The introduction of fertilizer runoff into a local pond ecosystem initially causes excessive growth of aquatic plants. Which of the following effects will the decay of the additional biomass from the aquatic plants most likely have on the pond ecosystem?
- increased numbers of carnivorous species as amphibian populations expand
- reduction in fish populations as a result of lower levels of dissolved oxygen
- expansion of herbivorous fish populations as primary productivity increases
- decreased populations of reptiles and amphibians as pond clarity is reduced
Answer to question 15
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0011) Phosphorus and nitrogen are nutrients in fertilizer runoff that can cause the eutrophication of freshwater bodies by stimulating the growth of algae. As the algae die and are consumed by bacteria, the increased population of bacterial decomposers uses up dissolved oxygen in the water, ultimately depriving fish populations of the oxygen they need to live.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0011) Phosphorus and nitrogen are nutrients in fertilizer runoff that can cause the eutrophication of freshwater bodies by stimulating the growth of algae. As the algae die and are consumed by bacteria, the increased population of bacterial decomposers uses up dissolved oxygen in the water, ultimately depriving fish populations of the oxygen they need to live.
Question 16
16. Phosphorus is an important nutrient for plants in the biologically rich Serengeti Plain in northern Tanzania. Phosphorus in this ecosystem is primarily derived from:
- lightning strikes that change atmospheric phosphorus into bioactive phosphate compounds.
- deposition of phosphate-rich marine aerosols and wind-blown dust during the dry season.
- fixation of elemental phosphorus in soil gases by microorganisms and detrivores.
- weathering of soils and the production of phosphorus-rich wastes from herds of herbivores.
Answer to question 16
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0011) The terrestrial component of the phosphorus cycle begins with phosphate-containing rocks and phosphates in soils derived from weathered rock. This is true for all terrestrial ecosystems. In the Serengeti Plain phosphorus is a limiting nutrient essential for the growth of plants that large herds of herbivores depend on for survival. As in other terrestrial ecosystems, some of the phosphorus is derived from the weathering of rocks; however, an additional source is the waste products of the herds of herbivores that feed on the grasses of the Serengeti Plain during seasonal migrations.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0011) The terrestrial component of the phosphorus cycle begins with phosphate-containing rocks and phosphates in soils derived from weathered rock. This is true for all terrestrial ecosystems. In the Serengeti Plain phosphorus is a limiting nutrient essential for the growth of plants that large herds of herbivores depend on for survival. As in other terrestrial ecosystems, some of the phosphorus is derived from the weathering of rocks; however, an additional source is the waste products of the herds of herbivores that feed on the grasses of the Serengeti Plain during seasonal migrations.
Question 17
17. The invasive Argentine ant is an omnivorous ant species widespread throughout the United States. These ants most often become a pest species as a result of which of the following adaptive behaviors common to many ant species?
- generating wings to migrate to new locations as flying ants
- leaving flooded nests and moving to dry locations
- transferring a queen to a new habitat as the population grows
- eating wood when other resources are diminished
Answer to question 17
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0011) Like many other types of ants, Argentine ants seek higher ground and dry locations during heavy rainfall events. Unfortunately for people, the dry location they find is often a home or business.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0011) Like many other types of ants, Argentine ants seek higher ground and dry locations during heavy rainfall events. Unfortunately for people, the dry location they find is often a home or business.
Question 18
18. Representative plants from both the tundra and the desert biomes are likely to possess which of the following adaptations?
- tall, flexible stems to better withstand wind
- large, showy flowers to encourage pollinators
- small, waxy leaves to prevent water loss
- deep, widespread roots to better access water
Answer to question 18
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0011) Biomes vary in both the abiotic and biotic factors that affect their inhabitants. One abiotic characteristic shared by both the tundra and desert biomes is low annual precipitation. The plants in both of these biomes often have small, waxy leaves, which minimizes evaporative water loss.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0011) Biomes vary in both the abiotic and biotic factors that affect their inhabitants. One abiotic characteristic shared by both the tundra and desert biomes is low annual precipitation. The plants in both of these biomes often have small, waxy leaves, which minimizes evaporative water loss.
Question 19
19. The vector diagram below shows vectors representing three forces acting on an object.
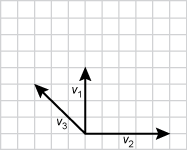
Each vector starts from the same origin, V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left.
Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the resultant vector representing the net force on the object?
-
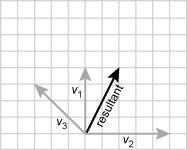 Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right two units and up four units.
Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right two units and up four units.
-
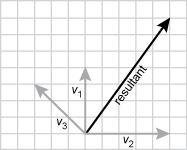 Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right five units and up seven units.
Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right five units and up seven units.
-
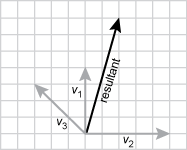 Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right two units and up seven units.
Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v one. the resultant vector goes right two units and up seven units.
-
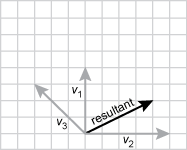 Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v two. the resultant vector goes right four units and up two units.
Each vector starts from the same origin. V one points straight up and is four units long. V two points to the right and is five units long. V three points to the upper left at a 45 degree angle and ends three units up and up three units left. the resultant vector is at an angle to the right between v one and v two closer to v two. the resultant vector goes right four units and up two units.
Answer to question 19
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0012) A vector is an arrow used to represent physical quantities that have both direction and magnitude, such as force. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force, while the direction of the arrow on a grid represents the direction in which the force acts. To determine the sum of several component vectors, the component vectors are added together by placing the tail (i.e., the beginning of the arrow) of one component vector at the head (i.e., the point of the arrow) of another vector without changing the direction of the moved vector. When all the component vectors are added (i.e., placed head to tail), the single resulting force is called the resultant vector.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0012) A vector is an arrow used to represent physical quantities that have both direction and magnitude, such as force. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force, while the direction of the arrow on a grid represents the direction in which the force acts. To determine the sum of several component vectors, the component vectors are added together by placing the tail (i.e., the beginning of the arrow) of one component vector at the head (i.e., the point of the arrow) of another vector without changing the direction of the moved vector. When all the component vectors are added (i.e., placed head to tail), the single resulting force is called the resultant vector.
Question 20
20. A car traveling on a winter day slides off an icy road as it tries to make a corner, continuing on a straight path until it comes to a stop. Which of the following laws of physics best describes the motion of the car as it slides off the road and continues along a straight path?
- Newton's first law (inertia)
- Newton's third law (action/reaction pairs)
- the first law of thermodynamics (conservation of energy)
- the second law of thermodynamics (entropy)
Answer to question 20
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0012) Newton's first law states that every body continues in its state of rest or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force exerted upon it. As a car tries to follow the curve in the road, the ice on the road reduces friction, allowing the car to continue in a straight line as described in Newton's first law.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0012) Newton's first law states that every body continues in its state of rest or of motion in a straight line at constant speed, unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force exerted upon it. As a car tries to follow the curve in the road, the ice on the road reduces friction, allowing the car to continue in a straight line as described in Newton's first law.
Question 21
21. A bicycle and bicyclist have a combined mass of 120 kg. If the bicyclist increases her velocity from 4 m/s to 8 m/s, what is the change in kinetic energy of the bicyclist and bicycle?
- 3840 J
- 2880 J
- 1920 J
- 960 J
Answer to question 21
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0012) The equation that is used to determine the kinetic energy of a system is
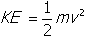 . In this case the starting kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist is
. In this case the starting kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist is
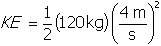 , while the kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist after accelerating is
, while the kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist after accelerating is
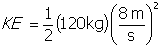 . To calculate the change in the system the difference in the two values must be determined with the following equation:
. To calculate the change in the system the difference in the two values must be determined with the following equation:
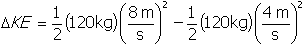 .
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0012) The equation that is used to determine the kinetic energy of a system is k e equals one half m v squared. In this case the starting kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist is k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator four m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared, while the kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist after accelerating is k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator eight m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared. To calculate the change in the system the difference in the two values must be determined with the following equation: delta k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator eight m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared minus one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator four m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared.
.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0012) The equation that is used to determine the kinetic energy of a system is k e equals one half m v squared. In this case the starting kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist is k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator four m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared, while the kinetic energy of the bicycle and bicyclist after accelerating is k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator eight m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared. To calculate the change in the system the difference in the two values must be determined with the following equation: delta k e equals one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator eight m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared minus one half open parenthesis one hundred and twenty k g close parenthesis open parenthesis start fraction numerator four m denominator s end fraction close parenthesis squared.
Question 22
22. A person leaves home and walks 5 blocks west, 4 blocks south, 5 blocks east, and 3 blocks north. Which of the following values represents their displacement?
- 1 block south
- 5 blocks west
- 10 blocks east
- 17 blocks north
Answer to question 22
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0012) Displacement is a vector, so it has direction as well as magnitude. Displacement measures the change in position of an object from the start to the end of its movement, but only looks at the total change. In this case, the movement to the west entirely cancels out the movement to the east. Additionally, part of the movement south is canceled out by the movement north so that 4 − 3 = 1.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0012) Displacement is a vector, so it has direction as well as magnitude. Displacement measures the change in position of an object from the start to the end of its movement, but only looks at the total change. In this case, the movement to the west entirely cancels out the movement to the east. Additionally, part of the movement south is canceled out by the movement north so that 4 minus 3 = 1.
Question 23
23. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
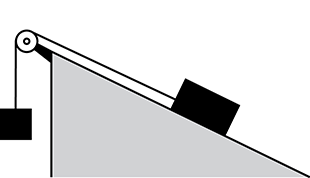
A hanging mass is suspended from the pulley and is parallel to the vertical side of the ramp. A block is connected to the pulley and lays along the surface of the ramp.
The diagram shows a wood block at rest on a ramp. It is attached to a rope, which passes through a pulley and attaches to a hanging mass. If the block is moved to any position on the ramp, the block remains in place. Which of the following statements correctly compares the weight of the hanging mass to the other forces involved?
- It is equal to the weight of the block.
- It is less than the normal force acting on the block.
- It is greater than the sum of the weight of the block and friction force between the block and ramp.
- It is equal to the sum of the normal force acting on the block and friction force between the block and ramp.
Answer to question 23
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0012) If the block can be moved to any position on the ramp and remain in place, the forces acting on the block must be balanced. The weight of the hanging mass must be opposed by forces equal to it. These forces include the normal force acting on the block and the force of static friction between the block and the ramp's surface.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0012) If the block can be moved to any position on the ramp and remain in place, the forces acting on the block must be balanced. The weight of the hanging mass must be opposed by forces equal to it. These forces include the normal force acting on the block and the force of static friction between the block and the ramp's surface.
Question 24
24. Each of the diagrams below illustrates an object between a magnifying lens and the focal point of the lens. The eye represents an observer looking at the object through the lens. Which of the following diagrams correctly shows the type of image formed and its position and orientation?
This item has four answer choices labeled A, B, C, and D. The diagrams for each of the four choices shows a double convex magnifying lens, an object, the eye of the observer, the focal point of the lens, and a real or virtual image seen by the observer. The four diagrams differ in the arrangement of these elements and whether the image is real or virtual. In all four diagrams, the observer's eye is the right-most element and is looking left.
-
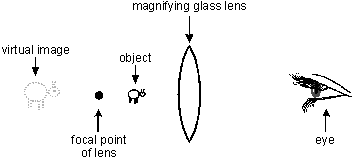 From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens, a virtual image that is erect and larger than the object.
From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens, a virtual image that is erect and larger than the object.
-
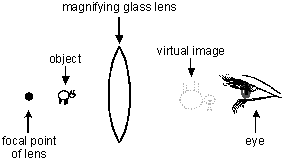 From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, a virtual image that is upside down and larger than the object, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens.
From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, a virtual image that is upside down and larger than the object, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens.
-
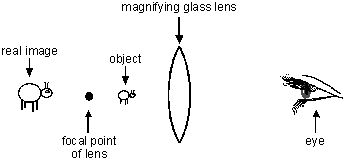 From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens, a real image that is erect and larger than the object.
From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens, a real image that is erect and larger than the object.
-
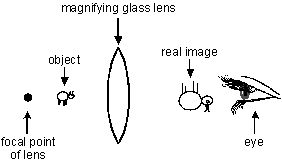 From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, a real image that is upside down and larger than the object, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens.
From right to left, the elements are: the observer's eye, a real image that is upside down and larger than the object, the lens, the object, the focal point of the lens.
Answer to question 24
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0013) When an object viewed through a convex lens is located between the focal point of the lens and the lens itself, the lens causes the light rays coming from the object to spread apart. This results in the formation of a virtual image, which appears to be on the same side of the lens as the object itself. This virtual image is upright and larger than the object, and thus the overall effect is one of magnification.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0013) When an object viewed through a convex lens is located between the focal point of the lens and the lens itself, the lens causes the light rays coming from the object to spread apart. This results in the formation of a virtual image, which appears to be on the same side of the lens as the object itself. This virtual image is upright and larger than the object, and thus the overall effect is one of magnification.
Question 25
25. The diagram shown below represents two transverse waves traveling toward each other at the same speed.
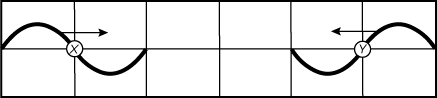
On the left, wave one is moving to the right toward wave two. Starting from the horizontal on the left side of the graph and heading to the right, wave one increases to a crest then decreases below the horizontal to a trough and then increases back up to the horizontal. The point in the middle where it crosses the horizontal is labeled X. On the right, wave two is moving to the left toward wave one. Starting from the horizontal on the right side of the graph and heading to the left, wave two increases to a crest then decreases below the horizontal to a trough and then increases back up to the horizontal. The point in the middle where it crosses the horizontal is labeled Y. The waves are reflections of each other over a vertical fold, where if one is up the other is down. The two waves have equal amplitudes of about half a unit.
Which of the following diagrams represents the wave pattern when the points marked X and Y overlap?
-
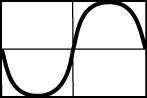 wave that starts decreasing below the horizontal to a trough then increases past the horizontal to a crest again then decreases back down to the horizontal. The amplitude of the wave is one unit.
wave that starts decreasing below the horizontal to a trough then increases past the horizontal to a crest again then decreases back down to the horizontal. The amplitude of the wave is one unit.
-
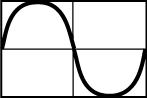 wave starts increasing to a crest, then decreases past the horizontal down to a trough then increases back up to the horizontal. the amplitude of the wave is one unit
wave starts increasing to a crest, then decreases past the horizontal down to a trough then increases back up to the horizontal. the amplitude of the wave is one unit
-
 just a straight line along the horizontal
just a straight line along the horizontal
-
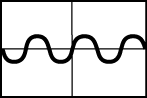 wave starts by decreasing to a trough below the horizontal then increasing past the horizontal up to a crest then decreasing back down past the horizontal to a trough then increasing back up past the horizontal to a crest then decreasing down past the horizontal down to a trough then increasing back up past the horizontal to a crest then finally decreasing back down to the horizontal. These are several smaller waves in the same distance where their amplitude is only about one fourth of a unit.
wave starts by decreasing to a trough below the horizontal then increasing past the horizontal up to a crest then decreasing back down past the horizontal to a trough then increasing back up past the horizontal to a crest then decreasing down past the horizontal down to a trough then increasing back up past the horizontal to a crest then finally decreasing back down to the horizontal. These are several smaller waves in the same distance where their amplitude is only about one fourth of a unit.
Answer to question 25
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0013) In the diagram, two transverse waves are traveling toward each other. When they overlap at the points marked X and Y, the trough of one wave will be superimposed on the crest of the other wave. This causes the two waves to cancel each other, producing a diagrammatic representation that is a flat line.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0013) In the diagram, two transverse waves are traveling toward each other. When they overlap at the points marked X and Y, the trough of one wave will be superimposed on the crest of the other wave. This causes the two waves to cancel each other, producing a diagrammatic representation that is a flat line.
Question 26
26. A person standing by the side of a road hears the siren of an approaching ambulance. Which of the following statements explains why the person hears the pitch of the siren increase as the ambulance approaches?
- Each successive sound wave has less distance to travel, so the crests of the sound waves are hitting the person's ear more frequently.
- As the speed at which the sound waves travel through the air increases, there is an increase in the frequency of the waves hitting the person's ear.
- Each successive sound wave is emitted nearer and nearer to the person, so the force of the waves as they hit the ear is greater.
- As the amplitude of the sound waves increases, there is a decrease in the wavelength of the sound waves hitting the person's ear.
Answer to question 26
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0013) Although the frequency emitted by the siren does not change as the siren approaches the person, the Doppler effect increases the frequency of the sound heard by the person. Since each sound wave generated by the siren is closer to the person than the previous sound wave, the sound waves hitting the person's ear arrive closer and closer together as the siren approaches, creating an increase in the frequency of the sound waves hitting the ear.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0013) Although the frequency emitted by the siren does not change as the siren approaches the person, the Doppler effect increases the frequency of the sound heard by the person. Since each sound wave generated by the siren is closer to the person than the previous sound wave, the sound waves hitting the person's ear arrive closer and closer together as the siren approaches, creating an increase in the frequency of the sound waves hitting the ear.
Question 27
27. The diagram below shows a ray of light shining into a fish tank.
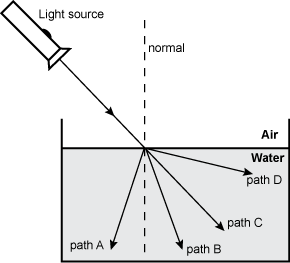
The single ray from the light source hits the surface of the water at about a forty five degree angle and then refracts. There are four paths below the water labeled A through D and a normal line shown as a vertical line that extends above and below the point where the ray hits the water. Path A points left at a small angle to the left of the normal line. Path B points right at a small angle to the right of the normal line. Path C follows the same path of the original light ray. Path D points right at a small angle just below the horizontal surface of the water.
Which of the following paths shown in the diagram best approximates the angle at which the original light ray is refracted as it crosses the air-water interface?
- path A
- path B
- path C
- path D
Answer to question 27
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0013) When light crosses a boundary between two different substances at an angle, the path of the light ray is bent because light travels at different speeds in substances with different optical densities. As the light ray shining on the water surface hits the surface at an angle, the path of the light is bent toward the normal according to Snell's law because water has a greater optical density than air. The greater optical density of water causes light to slow down as it moves across the air-water interface. Snell's law relates the angle at which a light ray hits a boundary surface to the angle of refraction within the material the light passes into.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0013) When light crosses a boundary between two different substances at an angle, the path of the light ray is bent because light travels at different speeds in substances with different optical densities. As the light ray shining on the water surface hits the surface at an angle, the path of the light is bent toward the normal according to Snell's law because water has a greater optical density than air. The greater optical density of water causes light to slow down as it moves across the air-water interface. Snell's law relates the angle at which a light ray hits a boundary surface to the angle of refraction within the material the light passes into.
Question 28
28. Use the diagram below to answer the question that follows.
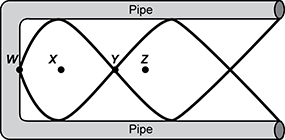
A diagram of a horizontal pipe with a harmonic standing wave is shown with four labeled points laid out horizontally through the pipe's middle. The harmonic waves intersect at the end of the pipe at point W. Moving along the horizontal length of the pipe, the waves move apart and together again. Where they reach their furthest distance apart, point X is located exactly in the middle. Point Y is located where the waves intersect halfway down the pipe. Finally, point Z is located in the middle of the waves as they begin to separate but before they are fully separated
The diagram represents a harmonic standing wave in a pipe filled with air. Disregarding the thermal motion of the air molecules, which statement best describes the motion of the air molecules in the pipe?
- molecules at point W move at the speed of sound
- molecules at point X vibrate faster than at point Y
- molecules at point Y were originally located at point W
- molecules at point Z are moving horizontally
Answer to question 28
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0013) Sound travels as the result of a series of compressions and rarefactions of air molecules. The areas of compressed air molecules push on the adjoining molecules, transferring energy and then the original molecules spread apart again. Thus, an individual air molecule oscillates in a back and forth direction.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0013) Sound travels as the result of a series of compressions and rarefactions of air molecules. The areas of compressed air molecules push on the adjoining molecules, transferring energy and then the original molecules spread apart again. Thus, an individual air molecule oscillates in a back and forth direction.
Question 29
29. The functioning of an electric motor is based on the principle that:
- charged particles flowing through a wire will be deflected by a magnetic field.
- magnetic field strength increases exponentially as distance from the field decreases.
- resistance to the flow of charge through a wire is proportional to the wire's diameter.
- current is induced in a wire that moves in and out of an alternating electrical field.
Answer to question 29
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0014) Charged particles moving through a magnetic field are deflected by the magnetic field. A current of charged particles moving through a wire is similarly deflected by a magnetic field. In an electric motor the deflection of a current-carrying wire by a magnetic field is used to move the coil of wire, turning electrical energy into kinetic energy. It is this relationship between electricity and magnetism that underlies the operation of an electric motor.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0014) Charged particles moving through a magnetic field are deflected by the magnetic field. A current of charged particles moving through a wire is similarly deflected by a magnetic field. In an electric motor the deflection of a current-carrying wire by a magnetic field is used to move the coil of wire, turning electrical energy into kinetic energy. It is this relationship between electricity and magnetism that underlies the operation of an electric motor.
Question 30
30. The diagram shows a parallel circuit and a series circuit. The lightbulbs and batteries are identical in both circuits.
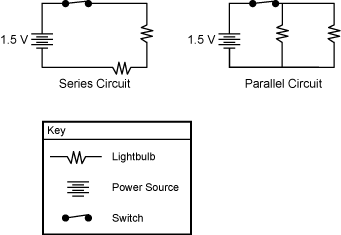
The Series Circuit has a one point five volt power source on the left, a lightbulb on the bottom, another light bulb on the right, and a closed switch on the top. The Parallel Circuit has a one point five volt power source on the left, two lightbulbs to the right on two parallel pathways, and a closed switch on the top before the lightbulbs.
Which of the following is primarily responsible for the fact that the lightbulbs in the parallel circuit are brighter than the lightbulbs in the series circuit?
- The voltage across each lightbulb in the series circuit is lower.
- The voltage across the entire series circuit is lower.
- The resistance of each lightbulb is lower in the parallel circuit.
- The resistance of the entire parallel circuit is lower.
Answer to question 30
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0014) Resistance is lowest in the parallel circuit because there are two separate pathways for the current, allowing it to draw more current from the power source and maximize the brightness of each bulb in the circuit.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0014) Resistance is lowest in the parallel circuit because there are two separate pathways for the current, allowing it to draw more current from the power source and maximize the brightness of each bulb in the circuit.
Question 31
31. Students observe that a plastic ruler that has been rubbed with a piece of wool attracts small bits of paper. The ruler attracts small bits of paper because:
- the paper exhibits properties that are associated with both insulators and conductors.
- protons and electrons in the paper become unequally distributed when the ruler is nearby.
- the ruler acts as a conductor and transfers electrons onto the pieces of paper.
- friction between the ruler and wool results in a build-up of protons in the ruler.
Answer to question 31
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0014) When a plastic ruler is rubbed with a piece of wool, some of the electrons from the atoms in the wool get transferred to the atoms in the ruler. The presence of the extra electrons creates an excess of negative charge on the ruler. When the plastic ruler is placed close to the small bits of paper, free electrons in the paper move away from the negatively charged ruler. The net effect is an attraction between the positively charged protons in the paper bits and the ruler.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0014) When a plastic ruler is rubbed with a piece of wool, some of the electrons from the atoms in the wool get transferred to the atoms in the ruler. The presence of the extra electrons creates an excess of negative charge on the ruler. When the plastic ruler is placed close to the small bits of paper, free electrons in the paper move away from the negatively charged ruler. The net effect is an attraction between the positively charged protons in the paper bits and the ruler.
Question 32
32. Students are experimenting with passing a bar magnet through the middle of a coil of wire. The wire coil is attached to an ammeter. This experiment is most appropriate for introducing students to which of the following concepts?
- Electrical energy can be converted to the movement of pistons in a motor.
- Voltage is the same across all components of a parallel circuit.
- Mechanical energy can be converted to electricity in a generator.
- Current in a conductor is directly proportional to the applied voltage.
Answer to question 32
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0014) As the students move the bar magnet in the activity described, they are changing the magnetic field surrounding the coiled wire. This results in the production of an electric current within the wire, which is measurable using an ammeter. Forming an electric current in this way is known as electromagnetic induction. A generator is a device that makes use of electromagnetic induction.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0014) As the students move the bar magnet in the activity described, they are changing the magnetic field surrounding the coiled wire. This results in the production of an electric current within the wire, which is measurable using an ammeter. Forming an electric current in this way is known as electromagnetic induction. A generator is a device that makes use of electromagnetic induction.
Question 33
33. During a unit on crime scene chemistry, students find a message written in blue ink on a piece of white paper. There are three different brands of blue-ink pens at the scene, and the students need to figure out which pen may have written the message. Which of the following techniques would be most appropriate for this activity?
- titration
- chromatography
- distillation
- electrophoresis
Answer to question 33
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0015) Paper chromatography is a technique which uses a stationary phase and a mobile phase to separate the components of a mixture, such as the dyes found in blue ink. This process involves placing a sample of each ink on chromatography paper (the stationary phase) and allowing a solvent (the mobile phase) to travel up the paper. The constituent dyes in the inks move at different rates with the solvent and are separated into different colored spots. The resulting pattern of spots allows comparison of the inks and could be used to match the ink used to write the message to the ink in a certain pen.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0015) Paper chromatography is a technique which uses a stationary phase and a mobile phase to separate the components of a mixture, such as the dyes found in blue ink. This process involves placing a sample of each ink on chromatography paper (the stationary phase) and allowing a solvent (the mobile phase) to travel up the paper. The constituent dyes in the inks move at different rates with the solvent and are separated into different colored spots. The resulting pattern of spots allows comparison of the inks and could be used to match the ink used to write the message to the ink in a certain pen.
Question 34
34. The table shown below lists the atomic numbers and mass numbers for four elements.
| Element |
O |
Na |
Al |
P |
| Atomic Number |
8 |
11 |
13 |
15 |
| Mass Number |
16 |
23 |
27 |
31 |
Which of the elements listed contains 16 neutrons in its nucleus?
- O
- Na
- Al
- P
Answer to question 34
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0015) An element's atomic number is equal to the number of protons present in the nucleus of one atom of that element. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons present in one atom of the element. The number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. In this example, phosphorus (P) is the only element with 16 neutrons (31 − 15 = 16).
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0015) An element's atomic number is equal to the number of protons present in the nucleus of one atom of that element. The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons present in one atom of the element. The number of neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom can be calculated by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number. In this example, phosphorus (upper P) is the only element with 16 neutrons (31 minus 15 = 16).
Question 35
35. The electron configurations and first ionization energies for sodium (Na) and potassium (K) are shown in the table.
| Element |
Electron Configuration |
First Ionization Energy (kJ/mol) |
| Na |
1s22s22p63s11 s squared, 2 s squared, 2 p to the power of 6, 3 s to the power of 1 |
495.9 |
| K |
1s22s22p63s33p64s11 s squared, 2 s squared, 2 p to the power of 6, 3 s cubed, 3 p to the power of 6, 4 s to the power of 1 |
418.7 |
Both of these elements lose their outermost electron and form ions with a +1 charge when they react with chlorine. The first ionization energy values indicate that more energy is required to remove the outermost electron of Na. Which of the following best explains why it takes more energy to form a Na+ superscript + ion than a K+ superscript + ion?
- The Na atom contains a greater number of protons.
- The valence electron of Na is closer to the positively charged nucleus.
- The Na atom has a total of three valence electrons.
- The electron configuration of the Na+ ion is the same as that for neon.
Answer to question 35
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: B. (Objective 0015) Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. Elements with more than one electron have multiple ionization energy values, each corresponding to different electrons. Ionization energies are a reflection of the attraction between an electron and the positively charged nucleus. The electron configurations of the two atoms show that the valence electron of Na, which is in a 3s orbital, is closer to the nucleus. As a result, the attraction between the valence electron of Na and its positively charged nucleus is greater than that of the valence electron of K and its nucleus. This stronger attraction means that more energy is required to remove the electron from the atom.
Correct Response: B. (Objective 0015) Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. Elements with more than one electron have multiple ionization energy values, each corresponding to different electrons. Ionization energies are a reflection of the attraction between an electron and the positively charged nucleus. The electron configurations of the two atoms show that the valence electron of Upper N a, which is in a 3 s orbital, is closer to the nucleus. As a result, the attraction between the valence electron of Upper N a and its positively charged nucleus is greater than that of the valence electron of upper K and its nucleus. This stronger attraction means that more energy is required to remove the electron from the atom.
Question 36
36. Cesium-137 has a half-life of 30 years. If a 2.00 mg sample of cesium-137 is placed in a sealed containment vessel, how much will be left in 120 years?
- 0.500 mg
- 0.250 mg
- 0.125 mg
- 0.0625 mg
Answer to question 36
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0015) The half-life of a radioisotope is the amount of time it takes for half of the radioisotope to decay. For cesium-137, the amount of radioisotope present will be reduced by half every 30 years. In this example, cesium-137 is allowed to decay for 120 years, or four half-lives. The amount of cesium-137 present in the vessel is reduced as follows: after 30 years 1.00 mg remains, after 60 years 0.500 mg remains, after 90 years 0.250 mg remains, and after 120 years 0.125 mg of cesium-137 remains.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0015) The half-life of a radioisotope is the amount of time it takes for half of the radioisotope to decay. For cesium-137, the amount of radioisotope present will be reduced by half every 30 years. In this example, cesium-137 is allowed to decay for 120 years, or four half-lives. The amount of cesium-137 present in the vessel is reduced as follows: after 30 years 1.00 m g remains, after 60 years 0.500 m g remains, after 90 years 0.250 m g remains, and after 120 years 0.125 m g of cesium-137 remains.
Question 37
37. A chemical substance with which of the following properties would be classified as a base?
- an aqueous substance that can accept hydrogen ions
- a substance that produces hydrogen ions during a reaction
- an ionic compound with a positive charge
- an element that reacts with negative ions to produce a neutral compound
Answer to question 37
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0016) According to the Brønsted-Lowry definition, acids and bases are substances that are defined in terms of their ability to donate or accept a hydrogen ion. Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions while bases accept hydrogen ions.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0016) According to the Brønsted-Lowry definition, acids and bases are substances that are defined in terms of their ability to donate or accept a hydrogen ion. Acids are substances that donate hydrogen ions while bases accept hydrogen ions.
Question 38
38. The chemical equation shown for the reaction between aluminum and hydrobromic acid is unbalanced.
Al(s) + HBr(aq) → AlBr3(aq) + H2(g)
Upper a l open parenthesis s close parenthesis plus upper h upper b r open parenthesis a q close parenthesis produces upper a l upper b r subscript three baseline open parenthesis a q close parenthesis plus upper h subscript two baseline open parenthesis g close parenthesis
If the reaction shown is balanced properly, which of the following coefficients would be placed before hydrobromic acid?
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 6
Answer to question 38
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: D. (Objective 0016) Atoms can be rearranged in chemical reactions, but they cannot be created or destroyed. This is why balanced chemical equations have the same number of atoms for each type of element on both the reactant side and product side of the reaction. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between aluminum and hydrobromic acid is
2Al(s) + 6HBr(aq) → 2AlBr3(aq) + 3H2(g).
This balanced equation indicates that the coefficient for HBr is 6.
Correct Response: D. (Objective 0016) Atoms can be rearranged in chemical reactions, but they cannot be created or destroyed. This is why balanced chemical equations have the same number of atoms for each type of element on both the reactant side and product side of the reaction. The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between aluminum and hydrobromic acid is two upper a l open parenthesis s close parenthesis plus six upper h upper b r open parenthesis a q close parenthesis produces two upper a l upper b r subscript three baseline open parenthesis a q close parenthesis plus three upper h sub two open parenthesis g close parenthesis. This balanced equation indicates that the coefficient for Upper H Upper B r is 6.
Question 39
39. The diagram shows the energy profile for a reaction carried out with and without a catalyst present.
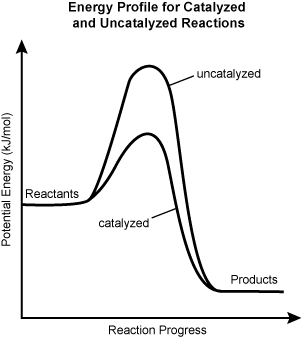
The potential energy in kilojoules per mole is on the y axis and the reaction progress is on the x axis. Both reactants start at the same y value and progress to the right horizontally at first. After some time the uncatalyzed and catalyzed parts of the graph split. The uncatalyzed line increases quickly up to a high crest then decreases quickly down below the initial y value. The catalyzed line increases to a crest that is lower than the uncatalyzed line, then decreases down below the initial y value to a point just above the x axis where it meets up with the uncatalyzed line again. The two lines then rejoin to form a single horizontal products line.
The energy profile shows that the catalyzed reaction requires less energy to proceed than the uncatalyzed reaction. This change in activation energy occurs because the catalyst:
- provides an alternative reaction mechanism.
- reduces the potential energies of the reactants.
- produces a different set of products.
- changes the reaction from endothermic to exothermic.
Answer to question 39
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: A. (Objective 0016) A minimum amount of energy must be present for a chemical reaction to proceed. This energy is referred to as activation energy. Catalysts lower the activation energy for a reaction by providing a different reaction mechanism for the reaction, one with lower activation energy.
Correct Response: A. (Objective 0016) A minimum amount of energy must be present for a chemical reaction to proceed. This energy is referred to as activation energy. Catalysts lower the activation energy for a reaction by providing a different reaction mechanism for the reaction, one with lower activation energy.
Question 40
40. Le Châtelier's principle can be used to predict how a system at equilibrium will respond to changes in temperature, pressure, or the concentration of reactants or products. The principle states that a system at equilibrium exposed to any of these external changes will respond by shifting its equilibrium position to counteract the effect of the change. According to Le Châtelier's principle, how will the equilibrium system shown below respond if N2 is added to the mixture?
2NO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇌ N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
two upper n upper o open parenthesis g close parenthesis plus two upper h subscript two baseline open parenthesis g close parenthesis in equilibrium with upper n subscript two baseline open parenthesis g close parenthesis two upper h subscript two basline upper o open parenthesis g close parenthesis
- The system will produce more H2 subscript 2 O.
- The forward and reverse reactions will cease.
- The system will produce more NO and H2 subscript 2 .
- The reaction between NO and H2 subscript 2 will increase.
Answer to question 40
- Answer Enter to expand or collapse answer. Answer expanded
- Correct Response: C. (Objective 0016) Adding N2 to the reaction mixture will lead to an increase in the concentration of N2. According to Le Châtelier's principle, the system will respond in a manner that reduces the concentration of N2. This can be achieved by shifting the equilibrium position to the left and producing more NO and H2.
Correct Response: C. (Objective 0016) Adding upper N subscript two to the reaction mixture will lead to an increase in the concentration of upper N subscript two. According to Le Châtelier's principle, the system will respond in a manner that reduces the concentration of upper N subscript two. This can be achieved by shifting the equilibrium position to the left and producing more upper N upper O and upper H subscript two.